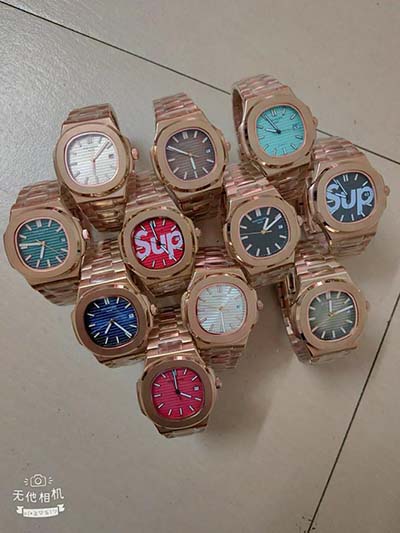
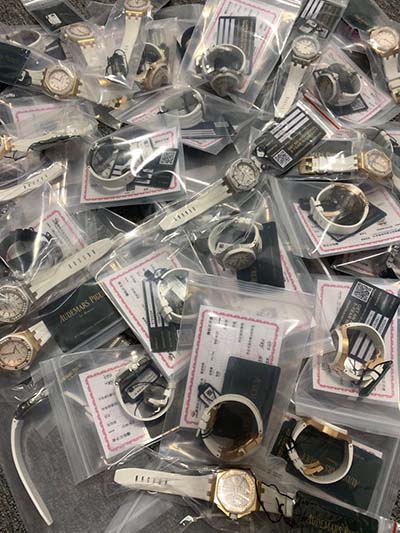
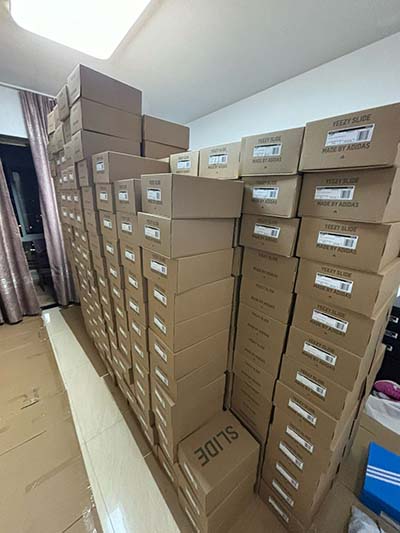
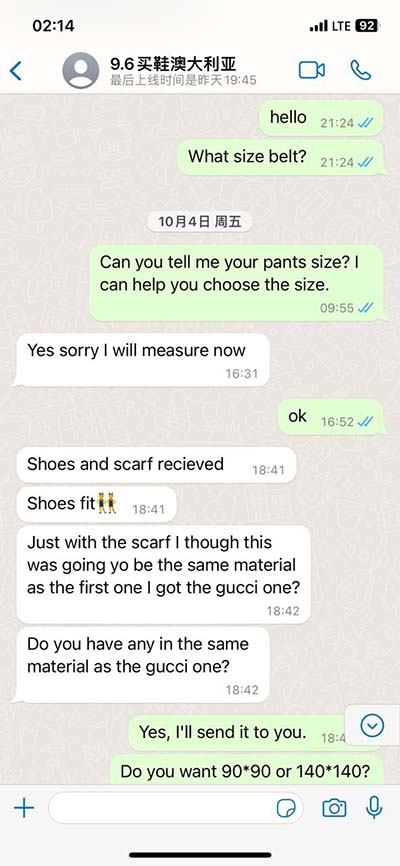
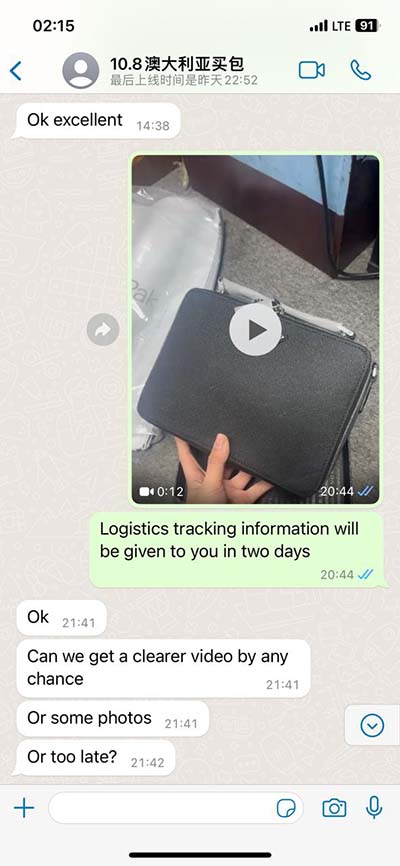
hermes psychopompus | hermes thoughts about inner self hermes psychopompus • Media related to Psychopomps at Wikimedia Commons See more $5,400.00
0 · what is hermes weakness
1 · what does psychopomp mean
2 · souls of the dead
3 · soul collector mythology
4 · psychopompos greek mythology
5 · hermes thoughts about inner self
6 · hermes myths of trickery
7 · hermes greek god trickster
The Sea-Dweller is definitely not the best-known Rolex watch. It sits far behind the everlasting Datejust, the presidential Day-Date, and the James Bond-esque Submariner.
Ancient religion Classical examples of a psychopomp are the ancient Egyptian god Anubis, the deity Pushan in Hinduism, the Greek ferryman Charon, the goddess Hecate, and god Hermes, the Roman god Mercury, the Norse Valkyries, the Aztec Xolotl, the Slavic goddess Morana and the Etruscan Vanth. . See morePsychopomps (from the Greek word ψυχοπομπός, psychopompós, literally meaning the 'guide of souls') are creatures, spirits, angels, demons, or deities in many religions whose responsibility is to escort newly . See more
• Life replacement narratives, Korean myths in which psychopomps are persuaded into sparing a person's life. See more• Geoffrey Dennis, "Abraham", "Elijah", "Lailah", "Sandalphon", Encyclopedia of Jewish Myth, Magic, and Mysticism, Llewellyn, 2007.• Eliade, Mircea, "Shamanism", 1964, Chapters 6 and 7, "Magical Cures: the Shaman as Psychopomp". See more• Media related to Psychopomps at Wikimedia Commons See moreHermes began as a god with strong chthonic, or underworld, associations. He was a psychopomp, leader of souls along the road between "the Under and the Upper world". This function gradually expanded to encompass roads in general, and from there to boundaries, travelers, sailors, commerce, and travel itself. Beginning with the earliest records of his worship, Hermes has been understo.
Classical examples of a psychopomp are the ancient Egyptian god Anubis, [3] the deity Pushan in Hinduism, the Greek ferryman Charon, [1] the goddess Hecate, and god Hermes, the Roman .
Greek god Hermes. Image credit: aszak - Pixabay. Like the Egyptian god Anubis, he is a psychopomp responsible for escorting newly deceased souls to the afterlife. As the .
Hermes began as a god with strong chthonic, or underworld, associations. He was a psychopomp, leader of souls along the road between "the Under and the Upper world". This .Hermes Psychopompus (Guide of Souls) sits on a rock preparing to lead the shade of a woman to the underworld. He hold's a herald's wand (kerykeion) in his hand. Hermes is also the protector of shepherds and the guide of souls in the abode of the dead. From this function comes his name Hermes Psychopompus, the Accompanier of .
Hermes held a unique position among the Olympian deities, serving various roles that reflected his diverse nature. Guide to the Underworld: Hermes was known as .In Greek mythology, Hermes was the psychopomp who guided the souls of the dead to the afterlife. He was also the god of commerce, thieves, and travelers. Hermes’ role as a .
Hermes Psychopomp (Guide of the Dead) leads the soul of a woman to the skiff of the ferryman Charon. The god wears a winged petasos cap and the ferryman stands in his boat holding a pole.
Known as Hermes Psychopompus, he guided the souls of the deceased to the afterlife, ensuring a safe passage to the realm of Hades. This dual role reflects the broader .Several scholars have claimed him as Hermes Psychopompus (e.g. Robert, Thanatos, 18; Clark and Coulson 1978:71). To the left, a young woman and a young man, identified as Memnon’s .
Classical examples of a psychopomp are the ancient Egyptian god Anubis, [3] the deity Pushan in Hinduism, the Greek ferryman Charon, [1] the goddess Hecate, and god Hermes, the Roman . Greek god Hermes. Image credit: aszak - Pixabay. Like the Egyptian god Anubis, he is a psychopomp responsible for escorting newly deceased souls to the afterlife. As the .
Hermes began as a god with strong chthonic, or underworld, associations. He was a psychopomp, leader of souls along the road between "the Under and the Upper world". This .Hermes Psychopompus (Guide of Souls) sits on a rock preparing to lead the shade of a woman to the underworld. He hold's a herald's wand (kerykeion) in his hand.
what is hermes weakness
Hermes is also the protector of shepherds and the guide of souls in the abode of the dead. From this function comes his name Hermes Psychopompus, the Accompanier of . Hermes held a unique position among the Olympian deities, serving various roles that reflected his diverse nature. Guide to the Underworld: Hermes was known as .In Greek mythology, Hermes was the psychopomp who guided the souls of the dead to the afterlife. He was also the god of commerce, thieves, and travelers. Hermes’ role as a .Hermes Psychopomp (Guide of the Dead) leads the soul of a woman to the skiff of the ferryman Charon. The god wears a winged petasos cap and the ferryman stands in his boat holding a pole.
Known as Hermes Psychopompus, he guided the souls of the deceased to the afterlife, ensuring a safe passage to the realm of Hades. This dual role reflects the broader .

chloe paddington real vs fake
chrome hearts replica hoodie

$18K+
hermes psychopompus|hermes thoughts about inner self